Navigation
Introduction
When an HTTP request is legitimate but the server’s current state prohibits it from being performed, the HTTP status code 409 Conflict response is used.
A conflict with the existing state of the target resource prevented the request from being completed. In cases where the user may be able to resolve the problem and retry the request, this code is used.
The server SHOULD provide a payload with enough information for a user to identify the conflict’s source.
The answer representation in this situation would most likely contain information useful for merging the discrepancies depending on the revision history.
General Understanding
This is very handy for APIs. Here are some potential examples:
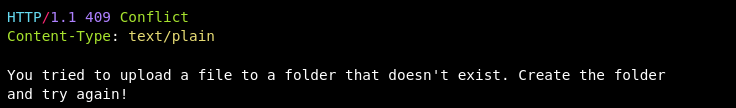
| 1. A user wishes to add a file to a folder that does not yet exist. 2. When you try to remove a bucket that isn’t empty, Amazon S3 utilizes it. 3. You’re writing a new blog article, but it’s about a category that’s been removed. |
The point here is that when this dispute is resolved, it may be feasible to perform the identical request again, for example:
| a. Creating the folder to which you want to upload. b. Before deleting the S3 bucket, make sure it’s empty. c.Re-assigning the category you’re seeking to assign to the blog post by creating or removing it. |
Example
In response to a PUT request, conflicts are most likely to arise.
For example, if versioning is utilized and the PUT representation includes modifications to a resource that contradict those made by a previous (third-party) request, the origin server may respond with a 409 signal that the request cannot be completed.
The response representation would most likely contain information useful for merging the differences based on the revision history in this case.
Status
| 409 Conflict |
Specifications
Browser compatibility
409 Code References
Rails HTTP Status Symbol :conflict
Go HTTP Status Constant http.StatusConflict
Symfony HTTP Status Constant Response::HTTP_CONFLICT
Python2 HTTP Status Constant httplib.CONFLICT
Python3+ HTTP Status Constant http.client.CONFLICT
Python3.5+ HTTP Status Constant http.HTTPStatus.CONFLICT
FAQs
Why does status code 409 conflict error occurs?
When an HTTP request is legitimate but the server’s current state prohibits it from being performed, the HTTP status code 409 Conflict occurs.
What is the example of HTTP Status Code 409?
In response to a PUT request, conflicts are most likely to arise.
For example, if versioning is utilized and the PUT representation includes modifications to a resource that contradict those made by a previous (third-party) request, the origin server may respond with a 409 signal that the request cannot be completed.
The response representation would most likely contain information useful for merging the differences based on the revision history in this case.
Related Post:
HTTP Status Code 300-Multiple Choices
HTTP Status Code 204 – No Content
HTTP Status Code 203 – Non-authoritative Information
HTTP Status Code 207 Multi-Status
HTTP Status Code 208 Already Reported
HTTP Status Code 400 Bad Request
HTTP Status Code 401 Unauthorized
HTTP Status Code 403 Forbidden Error
HTTP Status Code 404 Not Found
HTTP Status Code 405 Method Not Allowed
Conclusion
That should cover all the bases when it comes to HTTP Status code 409-conflict issues.
While there isn’t always much you can do when you get a 409 error, maybe some of these tips will come in handy the next time you get one. I hope this article was able to help you with your doubts and queries related to the HTTP status code 409( conflict).
Still, if there are any queries related to this topic, feel free to ask in the comment section, we would be happy to assist you. Thank you.


Kedar Dangal
Making a difference, Adding the sum.